Types of popular plastics & their common usages
Plastics are a group of materials that while being processed, can be formed into almost any desired shape and retain that shape. Plastics can be cast, moulded, or pressed into an unlimited variety of shapes. They are one of the most used materials on a volume basis in industrial and commercial life. Plastics are on par with metals, wood, and ceramics and are essential to the needs of virtually the entire spectrum of business. When properly applied, plastics will perform functions at a cost that other materials cannot match. Here we cover some of the popular plastics and their common usages.
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)

High Density Polyethylene is a polyethylene thermoplastic made from petroleum. HDPE is great for blow-moulding applications, particularly food and beverage containers because it won’t leach into the bottles’ contents. In addition, HDPE is recyclable which makes it a great choice for these disposable products.
HDPE is UV resistant which helps keep the products resistant from sunray’s damaging and discoloring effects. As it is resistant to chemicals, HDPE is great for laundry, shampoo, conditioner, household cleaning products, motor oil, antifreeze and recycling bins. The strength of these bottles is increased when they’ve been coloured or pigmented.
A higher molecular weight variant of HDPE is used for pipe grade sheet. This strengthening with its UV-resistance and ability to withstand high heat makes it ideal for piping and outdoor applications. It’s durable in most chemical interactions which make it useful in a lot of industrial applications.
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)

Low Density Polyethylene is used mainly in film applications for both packaging and non-packaging applications because of its good clarity and processability. Other markets include extrusion coatings, sheathing in cables and injection moulding applications.
It is used largely in food packaging applications such as meat and poultry wrapping, dairy products, snacks and sweets, frozen food bags and baked goods. It is used where high clarity films are required such as produce bags and bakery film. Non-food packaging applications include industrial liners, stretch- and shrink-wrap, garment bags and merchant bags.
Non-packaging film applications cover carry-out bags, waste bin liners and garbage bags, industrial sheeting, and construction and agricultural films.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)

PET is a clear, strong, and lightweight plastic that is widely used for packaging foods and beverages, especially convenience-sized soft drinks, juices and water. Today, more than half of the world's synthetic fiber is made from PET, which is called "polyester" when used for fiber or fabric applications.
PET containers are popular for packaging sodas, water, juices, salad dressings, cooking oil, peanut butter, shampoo, liquid hand soap, mouthwash, pharmaceuticals, even tennis balls. Virtually all single-serving and 2-liter bottles of carbonated soft drinks and water sold in the world are made from PET. Special grades of PET are used for carry-home prepared food containers that can be warmed in the oven or microwave.
Polypropylene Plastic (PP)

PP is one of the most commonly used thermoplastics in the world. Polypropylene uses range from plastic packaging, plastic parts for machinery and equipment and even fibres and textiles. It is a rigid, semi-crystalline thermoplastic that is used widely today in a range of domestic and industrial applications.
PP has a slippery, tactile surface, making it ideal for plastic furniture and low friction applications, such as gears in machinery and vehicles. It is highly resistant to chemical corrosion, making it an excellent choice for packaging for cleaning products, bleaches and first-aid products.
It offers excellent fatigue resistance and elasticity, securing it a well-deserved reputation for toughness and durability. Polypropylene has high insulation properties too, making it safe to use for plastic casing in electrical goods and cables. In its fibre form, polypropylene uses are not limited to not only useful for tote bags but also encompass a much wider range of other products, including ropes, twine, tape, carpets, upholstery, clothing and camping equipment. Its waterproof properties make it especially effective for the marine sector. In the automotive industry, polypropylene is also used widely, for example in for battery casings, trays and drink holders, bumpers, interior details, instrumental panels and door trims.
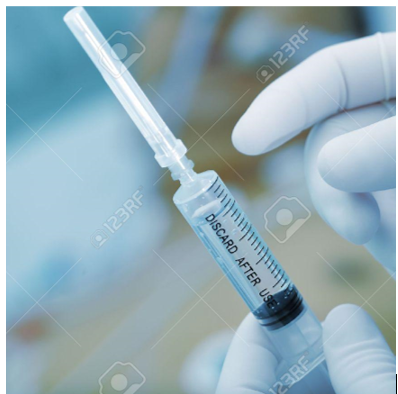
Finally, the medical world appreciates the waterproof properties of polypropylene too, as well as its flexible strength, resistance to mould, bacteria and chemical corrosion. It cleans well and can stand up to steam sterilisation methods. Some medical applications include syringes, medical vials, Petri dishes, pill containers and specimen bottles.
Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a versatile plastic used to make a wide variety of consumer products. As a hard, solid plastic, it is often used in products that require clarity, such as food packaging and laboratory ware. When combined with various colorants, additives or other plastics, polystyrene is used to make appliances, electronics, automobile parts, toys, gardening pots and equipment and more.
Polystyrene also is made into a foam material, called expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS), which is valued for its insulating and cushioning properties. Foam polystyrene can be more than 95 percent air and is widely used to make home and appliance insulation, lightweight protective packaging, surfboards, foodservice and food packaging, automobile parts, roadway and roadbank stabilization systems and more.

Polystyrene is used in appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, ovens, microwaves, vacuum cleaners, blenders – these and other appliances often are made with polystyrene (solid and foam) because it is inert (doesn’t react with other materials), cost-effective and long-lasting.
It is also used to make many car parts, including knobs, instrument panels, trim, energy absorbing door panels and sound dampening foam. Foam polystyrene also is widely used in child protective seats.
Polystyrene is used for the housing and other parts for televisions, computers and all types of IT equipment, where the combination of form, function and aesthetics are essential.
Polystyrene is solid and foam forms are widely used to protect consumer products. CD and DVD cases, foam packaging peanuts for shipping, food packaging, meat/poultry trays and egg cartons typically are made with polystyrene to protect against damage or spoilage.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is another one of the most widely used polymers in the world. Due to its versatile nature, PVC is used extensively across a broad range of industrial, technical and everyday applications including widespread use in building, transport, packaging, electrical/electronic and healthcare applications.
PVC is a very durable and long lasting material which can be used in a variety of applications, either rigid or flexible, white or black and a wide range of colours in between.

Economical, versatile polyvinyl chloride (PVC, or vinyl) is used in a variety of applications in the building and construction, health care, electronics, automobile and other sectors, in products ranging from piping and siding, blood bags and tubing, to wire and cable insulation, windshield system components and more.
Due to its versatility, plastics in its many forms are used nearly everywhere in our daily lives. It has brought us many benefits in the production of goods and the goods themselves. The demand for plastics will continue to grow as it is an essential ingredient in most industries and there are virtually no materials that can replace it.